Metal Salts
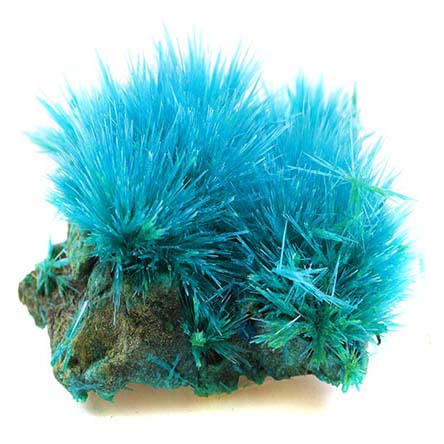

Copper(II) chloride dihydrate | CuCl2·2H2O | Purity: 99.8%
Appearance: Blue to green solid | Melting point: 430°C | Boiling point: 1490°C
Copper (II) chloride is used as a catalyst for organic and inorganic reactions, mordant for dyeing and printing of textiles, pigment for glass and ceramics, wood preservative, disinfectant, insecticide, fungicide, and herbicide, and as a catalyst in the production of chlorine from hydrogen chloride. Other important applications are in copper plating of aluminum, preparation of copper standard solutions, testing for molybdenum, in tinting-baths for iron and tin, in pigments for ceramics and glasses, as a fixer and desensitizer reagent in photography, in mercury extraction from ores, in laundry-marking and invisible inks, and in the manufacture of various copper salts.
| Cu | Al | Na | Ca | Mn | Fe | Mg | Zn | Pb |
| >36.9 % | 20 ppm | 15 ppm | <0.1 % | <1 ppm | <25 ppm | <10 % | <30 ppm | <10 ppm |
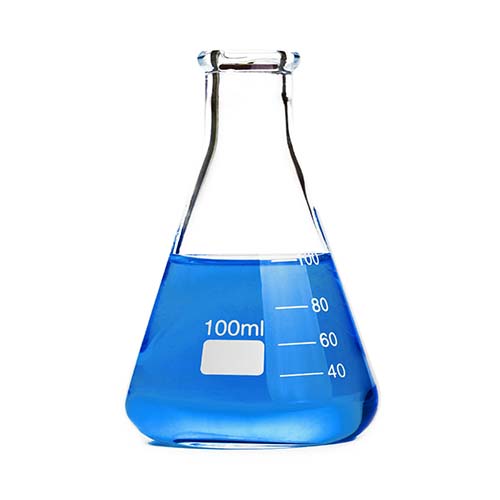

Copper tetrafluoroborate | Cu(BF4)2 | Purity: 40% – 42%
Appearance: Dark-blue odorless aqueous solution | Melting point: -90°C | Boiling point: 130°C
Copper(II) tetrafluoroborate is commonly used as a copper electroplating material and in the production of printed circuits. It is also deployed as a component of fluxing, as a catalyst and as an active filler in resin bonded abrasives. In organic chemistry laboratories, it is used to facilitate synthetic reactions such as the Diels-Alder reaction.
| Cu | Al | Na | Ca | Mg | Fe | B(OH)3 | Ni | Rem. (water) |
| >13 % | 20 ppm | 10 ppm | <0.2 % | <1 ppm | <10 ppm | <2 % | <5 ppm | 50-52 % |
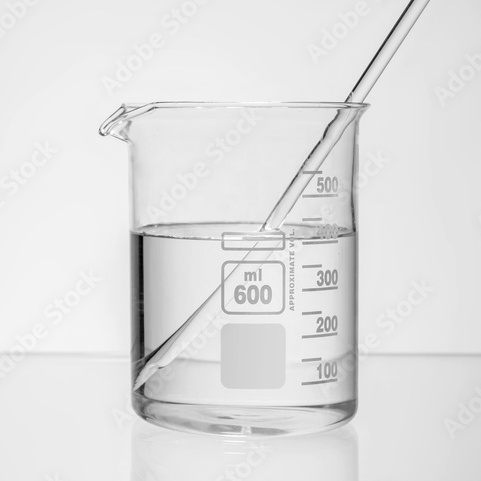

Lead fluoroborate | Pb(BF4)2 | Purity: 40% – 45%
Appearance: Colourless liquid | Melting point: -90°C | Boiling point: 130°C
Lead fluoborate is a crystalline powder that is normally disolved in a water solution. It is used as an electroplating solution for metal objects, as a curing agent for epoxy resins and a catalyst in the production of linear polyesters.
| Cu | Al | Na | Ca | Mg | Fe | B(OH)3 | Pb | Rem. (water) |
| <1 % | 20 ppm | 10 ppm | <0.2 % | <1 ppm | <10 ppm | <2 % | >11 % | 50-52 % |

Nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate | NiCl2·6H2O | Purity: –
Appearance: Green monoclinic crystals | Melting point: 140°C | Boiling point: N/A
Nickel chloride is used for nickel plating cast zinc, as an agent in electrolytic refining of nickel, as a chemical intermediate for nickel catalysts and complex nickel salts, and as an absorber of ammonia gas in industrial gas masks, among other uses.
| Pb | Fe | Cu | Cd | Co | As | Ni | Zn |
| <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.00005 | <0.00004 | <0.0002 | <0.0005 | 24.66 | <0.00005 |
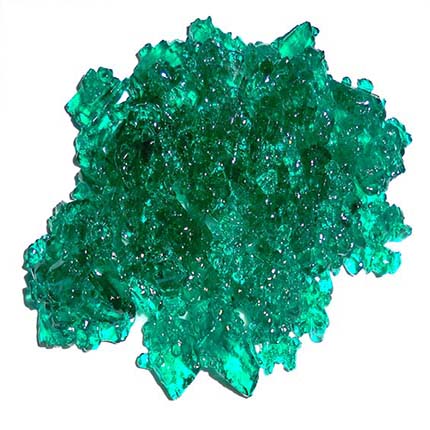

Nickel nitrate hexahydrate | Ni(NO3)2·6H2O | Purity: >99.84%
Appearance: Emerald green hygroscopic solid | Melting point: 56.7°C | Boiling point: 136.7°C
Nickel nitrate is used in the preparation of nickel-impregnated catalysts. It also is used to make nickel plates in nickel-cadmium batteries. Other applications are in ceramics to produce brown colors and in preparing nickel oxide.
| Cu | Sn | Ba | Pb | Mn | Ca | Mg | Co | Sr |
| 2.7 ppm | <0.6 ppm | <1.8 | 3.2 ppm | 2.5 ppm | <5 ppm | <1 ppm | <0.4 ppm | <2.5 ppm |
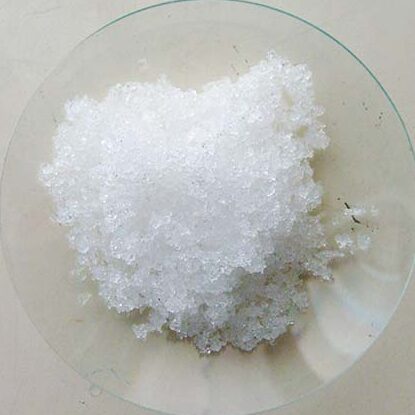

Silver nitrate | AgNO3 | Purity: >99.995%
Appearance: White crystalline solid | Melting point: 212°C | Boiling point: 440°C
Silver nitrate is a natural compound with antiseptic activity. It can be used as a cauterizing or sclerosing agent and can help create a scab to help stop bleeding from a minor skin wound. In its solid form, silver nitrate is commonly used as a precursor to other silver-containing compounds. It is used in making photographic films and in laboratory setting as a staining agent in protein visualization in PAGE gels and in scanning electron microscopy.
| Cu | Al | Sr | Pb | Mg | Cd | Zn | Co | Ni |
| <10 ppm | <1 ppm | 1.5 ppm | <0.1 ppm | <1 ppm | <0.1 ppm | <5 ppm | <0.1 ppm | <0.1 ppm |
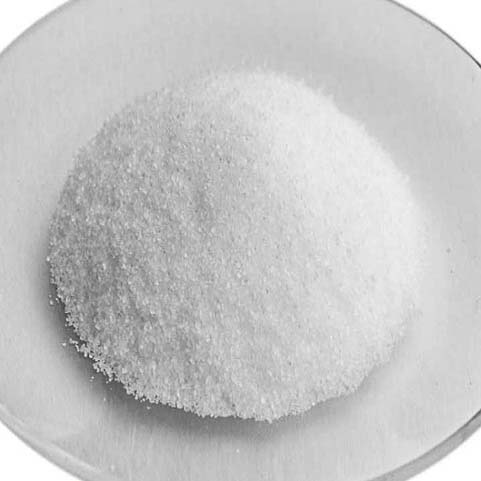

Stannous chloride dihydrate | SnCl2·2H2O | Purity: >99.71%
Appearance: White to almost white powder to crystal | Melting point: 247°C | Boiling point: 623°C
As a solution, stannous chloride containing a little hydrochloric acid is used for the tin-plating of steel, in order to make tin cans. An electric potential is applied, and tin metal is formed at the cathode via electrolysis. Other uses include the deployment as a mordant in textile dyeing to impart brighter colours with some dyes such as cochineal.
| Cu | Al | Fe | Pb | Mg | Fe | Zn | Co | Ni |
| <1 ppm | <23 ppm | <0.00002 % | <66 ppm | <19 ppm | <30 ppm | <1 ppm | <1 ppm | <1 ppm |
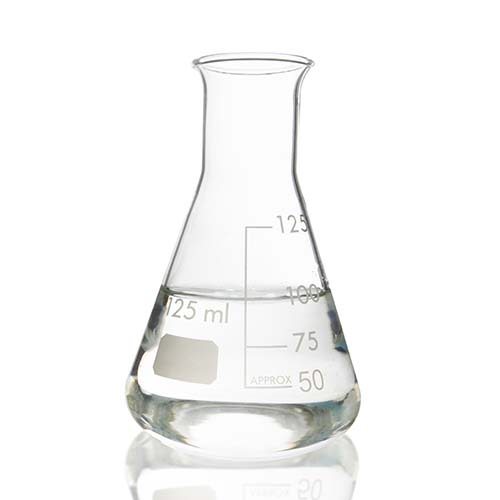

Tin tetrafluoroborate | Sn(BF4)2 | Purity: 40% – 45%
Appearance: Colourless liquid | Melting point: -90°C | Boiling point: 130°C
Stannous (tin) fluoroborate is most commonly used as an electrolyte in electroplating for tin and is also used with lead fluoroborate for lead-tin plating. It is also used for plating bath tinned copper, tin and tin alloy. Furthermore, it acts as a catalyst for various organic reactions. It is also used as a petrochemical additive.
| Cu | Al | Na | Ca | Mg | Fe | B(OH)3 | Sn | Rem. (water) |
| <1 % | 20 ppm | 10 ppm | <0.2 % | <1 ppm | <10 ppm | <2 % | >16 % | 50-52 % |